(1 of 8)
Base Quantities
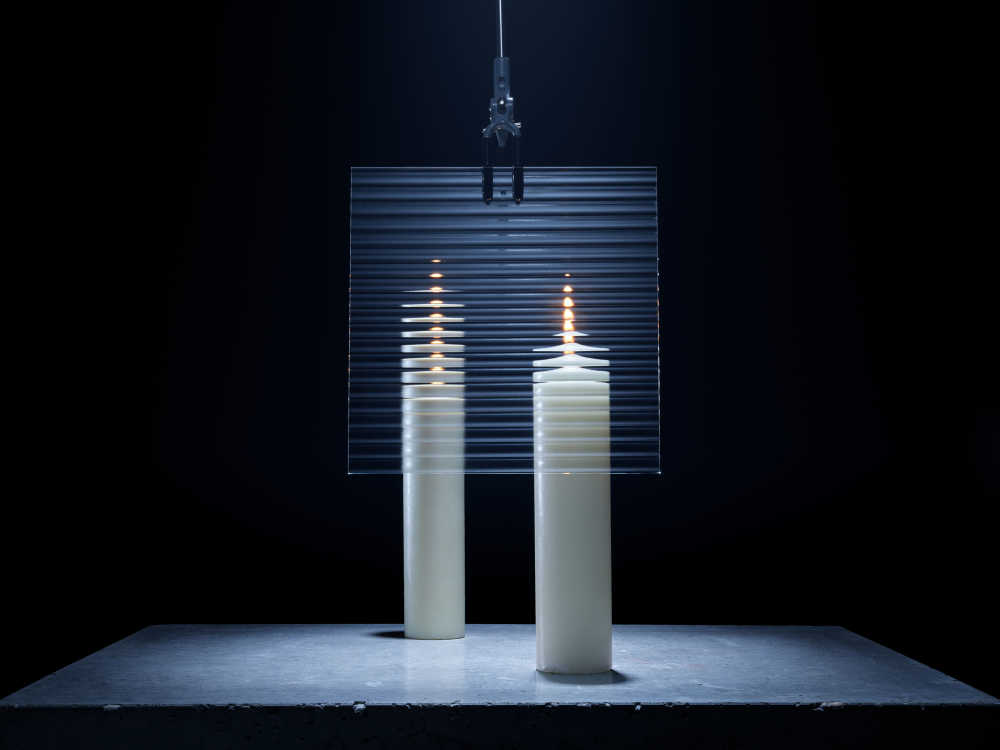
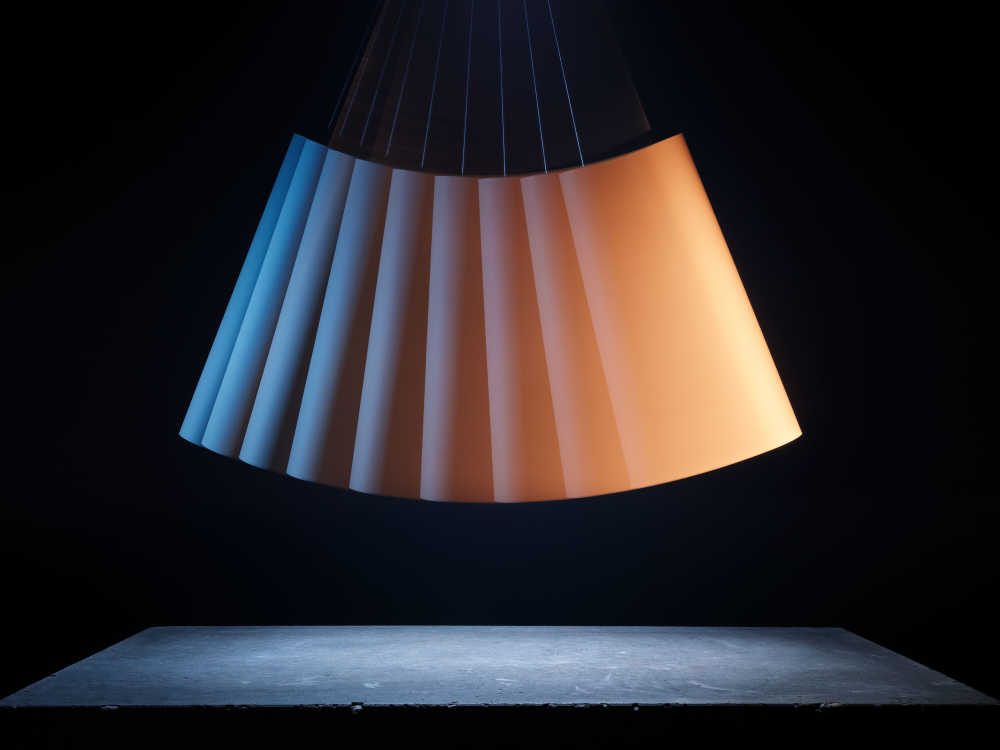
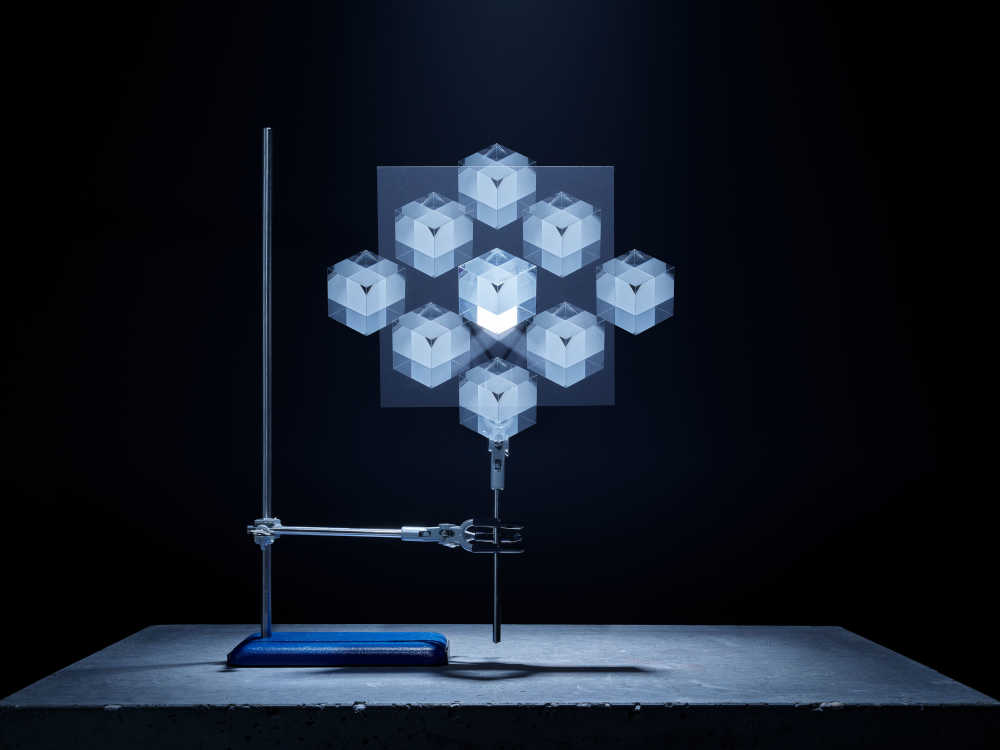
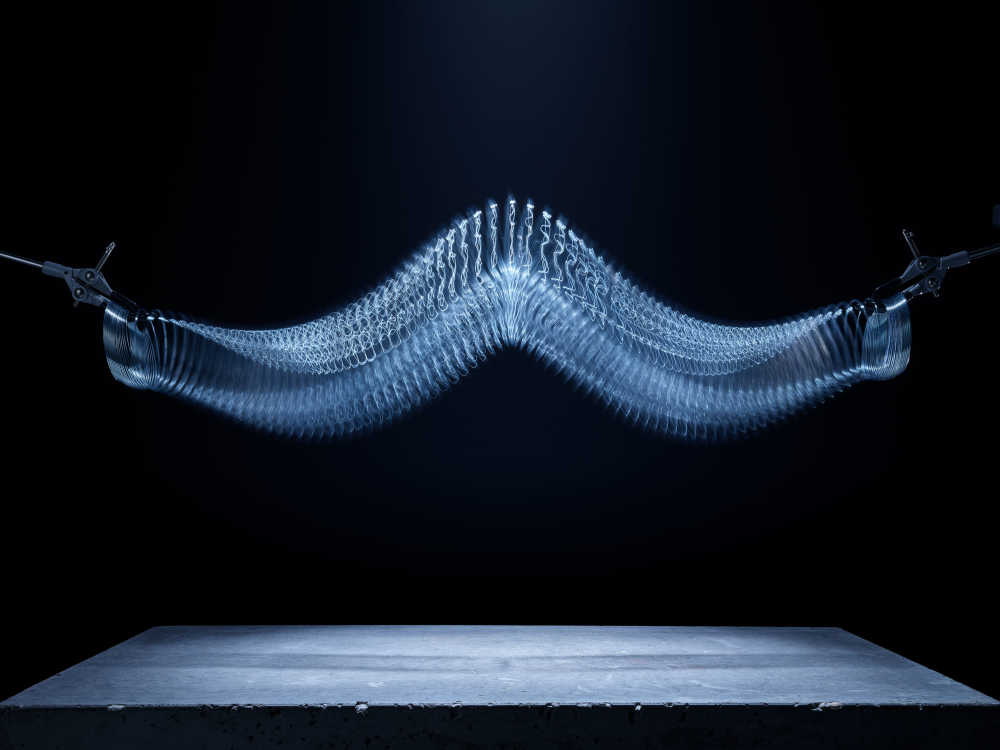
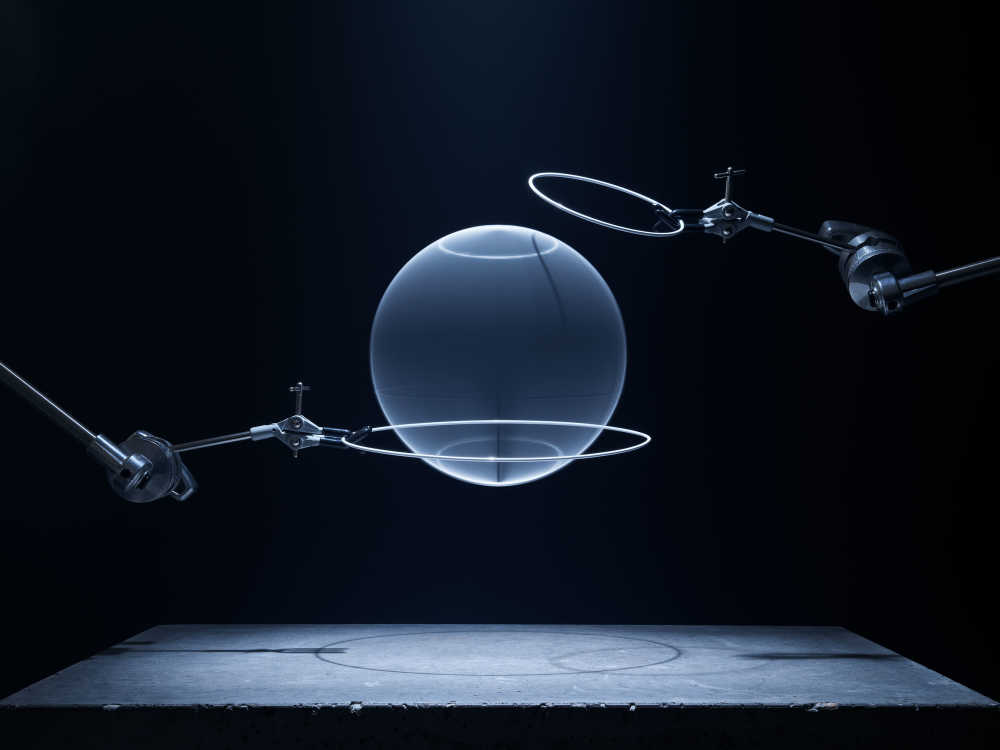
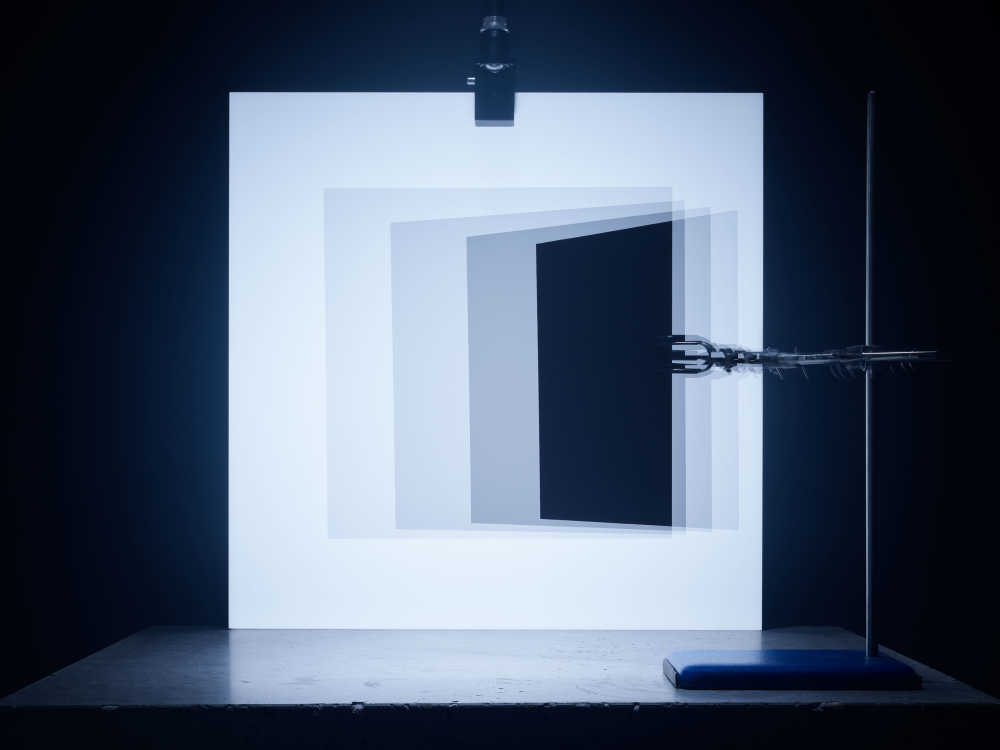
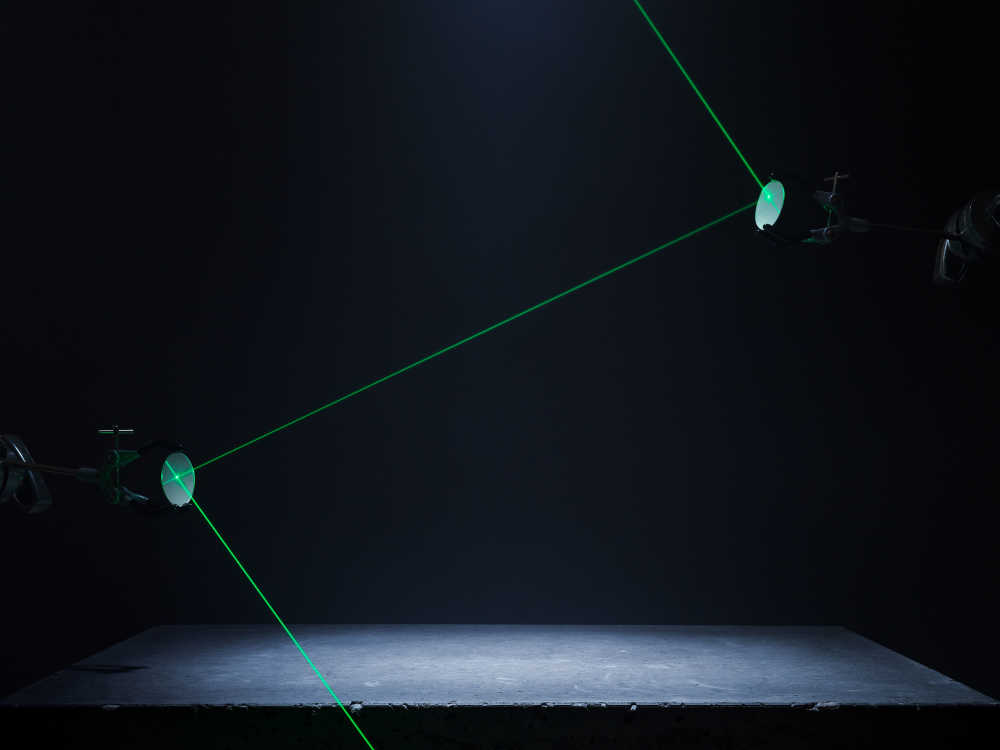
Captured entirely in camera this project playfully visualises using creative photographic techniques the seven base quantities. Inspired by the work of Berenice Abbot whose documenting science images brought wider understanding to the otherwise complicated world of physics.
A base quantity is a physical quantity in a subset of a given system of quantities that is chosen by convention, where no quantity in the set can be expressed in terms of the others. The International System of Quantities (ISQ) defines seven base quantities:
Electric current: a flow of electric charge in a circuit.
Length: a measure of distance.
Luminous intensity: a measure of the wavelength-weighted power emitted by a light source in a particular direction.
Mass: a property of a physical body and a measure of its resistance to acceleration (a change in its state of motion) when a net force is applied.
Amount of substance: a measure of the size of an ensemble of elementary entities, like a collection of atoms, molecules or other particles.
Thermodynamic temperature: is defined by the third law of thermodynamics in which the theoretically lowest temperature is the zero point. At this point, absolute zero, the particle constituents of matter have minimal motion and can become no colder.
Time: is the indefinite continued progress of existence and events that occur in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future.